728x90
SMALL
목표
- 인터페이스 Queue의 관련 메소드를 알아보자.
- Queue를 LinkedList로 구현해보자.

Queue 인터페이스
자바(Java)에서 Queue는 데이터를 저장하고 관리하는 자료 구조로, FIFO(First-In-First-Out) 원칙을 따릅니다.
큐는 요소(element)들의 집합으로 생각할 수 있으며,
새로운 요소는 항상 큐의 뒤쪽에 추가되고, 기존 요소들은 앞쪽에서부터 순차적으로 제거됩니다.

아래는 Queue인터페이스에서 일부 설명을 가져온 내용입니다.
ublic interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> {
/**
* @throws IllegalStateException – if the element cannot be added at this time due to capacity
*/
boolean add(E e);
/**
* @Returns true if the element was added to this queue, else false
*/
boolean offer(E e);
/**
* @return the head of this queue
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty
*/
E remove();
/**
* @return the head of this queue, or {@code null} if this queue is empty
*/
E poll();
/**
* @return the head of this queue
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty
*/
E element();
/**
* @return the head of this queue, or {@code null} if this queue is empty
*/
E peek();
}Queue관련 메소드
add(element)또는offer(element)
: 요소를 큐의 뒤쪽에 추가하며, 성공적으로 추가되었으면 true를 반환합니다.add()메서드: 요소를 추가할 수 없는 경우 예외(IllegalStateException)가 발생합니다.offer()메서드: 요소를 추가하고 성공 여부(boolean값)를 반환합니다.
remove()또는poll(): 첫 번째 요소를 제거하고 반환합니다.remove()메서드: 큐가 비어있을 때 예외(NoSuchElementException)가 발생합니다.poll()메서드: 큐가 비어있으면null값을 반환합니다.
element()또는peek(): 큐의 첫 번째 요소(헤드)를 가져옵니다.element(): 비어있다면 예외(NoSuchElementException)가 발생합니다.peek()메서드: 비어있다면null을 반환합니다.
LinkedList로 Queue 구현하기
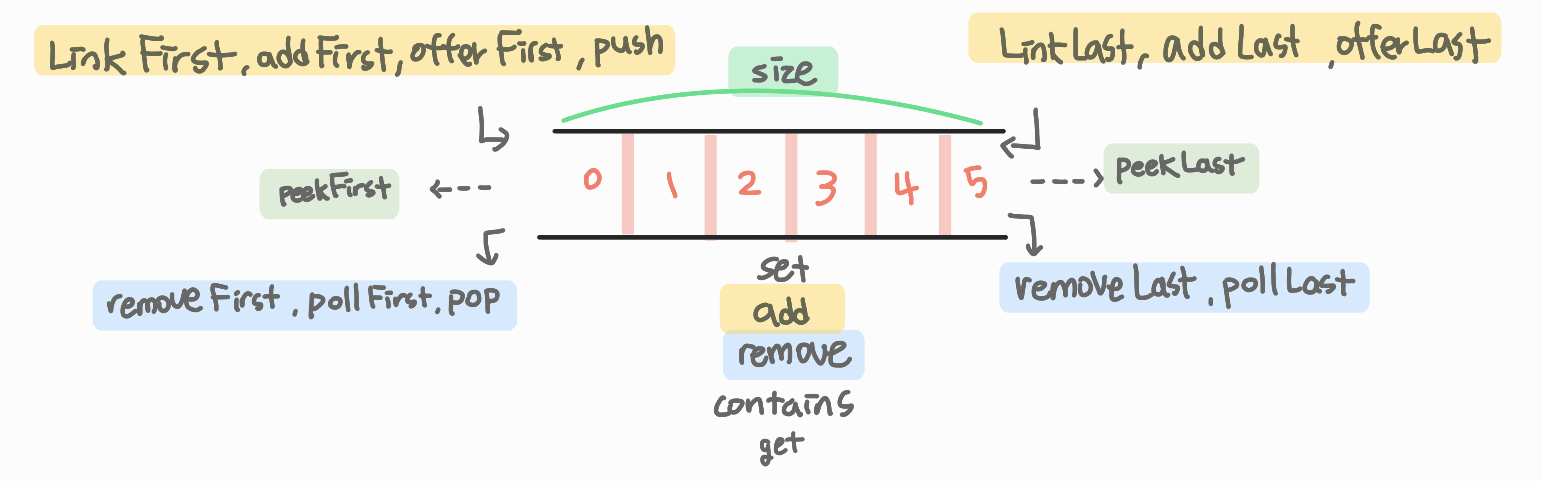
LinkedList는 Deque를 구현하고
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.SerializableDeque은 Queue를 상속받기 때문에
public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E>LinkedList를 이용하여 Queue를 구현할 수 있습니다.
예시
아래는 LinkedList로 Queue를 구현하는 예시입니다.
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add("A");
queue.add("B");
queue.add("C");
// "B" 요소의 index 검색
int indexOfB = ((LinkedList<String>) queue).indexOf("B");
System.out.println(indexOfB); // 출력: 1
}
}
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
// add: 리스트의 끝에 요소 추가
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
// peek: 리스트의 첫 번째 요소를 반환 (제거하지 않음)
Integer firstElement = list.peek();
System.out.println("Peek (첫 번째 요소): " + firstElement); // 출력: 1
// addFirst: 리스트의 첫 번째 위치에 요소 추가
list.addFirst(0);
// peekFirst: 리스트의 첫 번째 요소를 반환 (제거하지 않음)
Integer firstElementAfterAddFirst = list.peekFirst();
System.out.println("PeekFirst (첫 번째 요소): " + firstElementAfterAddFirst); // 출력: 0
// addLast: 리스트의 끝에 요소 추가
list.addLast(4);
// peekLast: 리스트의 마지막 요소를 반환 (제거하지 않음)
Integer lastElement = list.peekLast();
System.out.println("PeekLast (마지막 요소): " + lastElement); // 출력: 4
// 최종 리스트 출력
System.out.println("최종 리스트: " + list);
}
}728x90
LIST
'Language > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Effective Java] private 생성자와 열거 타입으로 싱글턴 보증하기 (0) | 2023.08.10 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA][자료구조] Stack (0) | 2023.08.09 |
| [Effective java] 정적 팩터리 메서드 (0) | 2023.07.29 |
| [Effective java] private 생성자 - 인스턴스화 막기 (0) | 2023.07.28 |
| [JAVA] Comparator, Comparable을 이용해서 배열과 List를 정렬하자. (0) | 2023.07.28 |
